
The kidneys also manage fluid balance by regulating urine production.

Feedback Mechanisms: Homeostasis control relies heavily on feedback mechanisms.Here are a few ways the body controls homeostasis: Numerous physiological processes cooperate to monitor and control physiological variables as part of the maintenance of homeostasis.
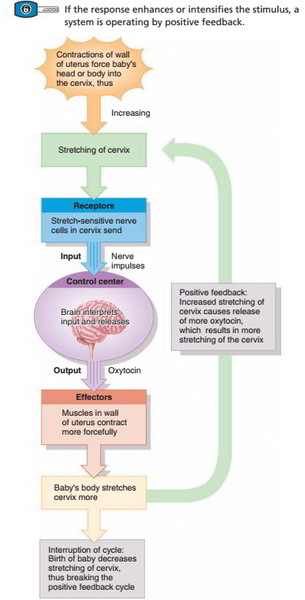
The body reacts to fluid loss by raising thirst and secreting hormones that encourage the retention of water and electrolytes, such as when sweating or urinating.To maintain perfect hydration and electrolyte concentrations in the blood and tissues, the body controls the balance of fluids and electrolytes.The body reacts to a reduction in blood pressure, such as occurs during sleep or relaxation, by slowing the heart rate and dilation of blood vessels to enhance blood flow.The body reacts to high blood pressure by speeding up the heartbeat and tightening blood vessels to maintain blood flow, such as during physical exertion or times of stress.The body controls blood pressure to ensure that tissues and organs receive the right amount of blood. On the other hand, when the pH levels rise too high, the body reacts by slowing down breathing to hold onto carbon dioxide, which can result in alkalosis.The body responds by speeding up breathing to get rid of extra carbon dioxide, which can lead to acidosis, when the pH levels become excessively acidic.The blood and tissues in the body are kept at a slightly alkaline pH to guarantee its optimal functioning. When blood sugar levels fall, the pancreas secretes glucagon, which prompts the liver to release glucose that has been stored there.The pancreas releases insulin to facilitate the absorption of glucose by cells when blood sugar levels rise, such as after a meal.In order to maintain a consistent supply of energy for the cells, the body closely controls blood glucose levels. On the other hand, when the body temperature decreases, the body reacts by shivering in an effort to produce heat.The body reacts to an increase in body temperature by increased perspiration to cool down, such as during exercise or a fever.It includes controlling a number of physiological parameters, including glucose levels, pH, and temperature.Įxamples of Homeostasis in Human Body Body Temperatureīy controlling the flow of heat into and out of the body, the body keeps its internal temperature at around 98.6☏ (37☌).In order to maintain a consistent internal environment, it uses feedback controls and other regulatory processes.Homeostasis is a self-regulating mechanism that controls the internal factors required for sustaining life.Homeostasis is the maintenance of consistent internal chemical and physical state by a living being in response to the changing conditions to survive and function optimally.Feedback loops are employed to maintain the steady state of Homeostasis. Homeostasis is any strategy used by living creatures to actively maintain the relatively consistent conditions required for existence. The environment of the Earth is dynamically kept in a stable state by similar mechanisms.His book the “Wisdom of the Body” explains how the human body maintains constant blood oxygen levels, water, salt, sugar, protein, and fat levels, as well as body temperature. Walter Cannon first used the word in 1930.

Homeostasis is derived from the ancient Greek words ὅμοιος (pronounced: hómoios) and ἵστημι (pronounced: hístēmi), which means “ same” and “ steady”.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
